* objectify app away from window. wip * fix messaging obj binding; put logo behind video; fix /null issue with temp logo image * first pass at js refactor * remove unused files that had been consolidated during refactor * set up vue before getting config * add a few comments * dont use big arrow function, just bind, for safari * add airplay after instantiating video; check if input exists before disabling it;: * only set poster on pause during playback, and onEnded; take out sample videoJS tech options * disable chat after 5mins after going offline * move 'online' class to video container as it conflicts with dynamically change classnames from non-vue sources * disable chat based on lastdisconnecttime * fix typo; do offline mode onEnded instead of status offline * move offline ui display things to offline mode function; move poster setting on pause to main app to keep player obj cleaner; use opacity to hide video element on offline as sometimes control bars may still linger with vis:hidden * fixes' * don't autoplay. just show play button when stream is online so that it's easier to start playign without looking for the unmute button * clean up console logs Co-authored-by: Gabe Kangas <gabek@real-ity.com>
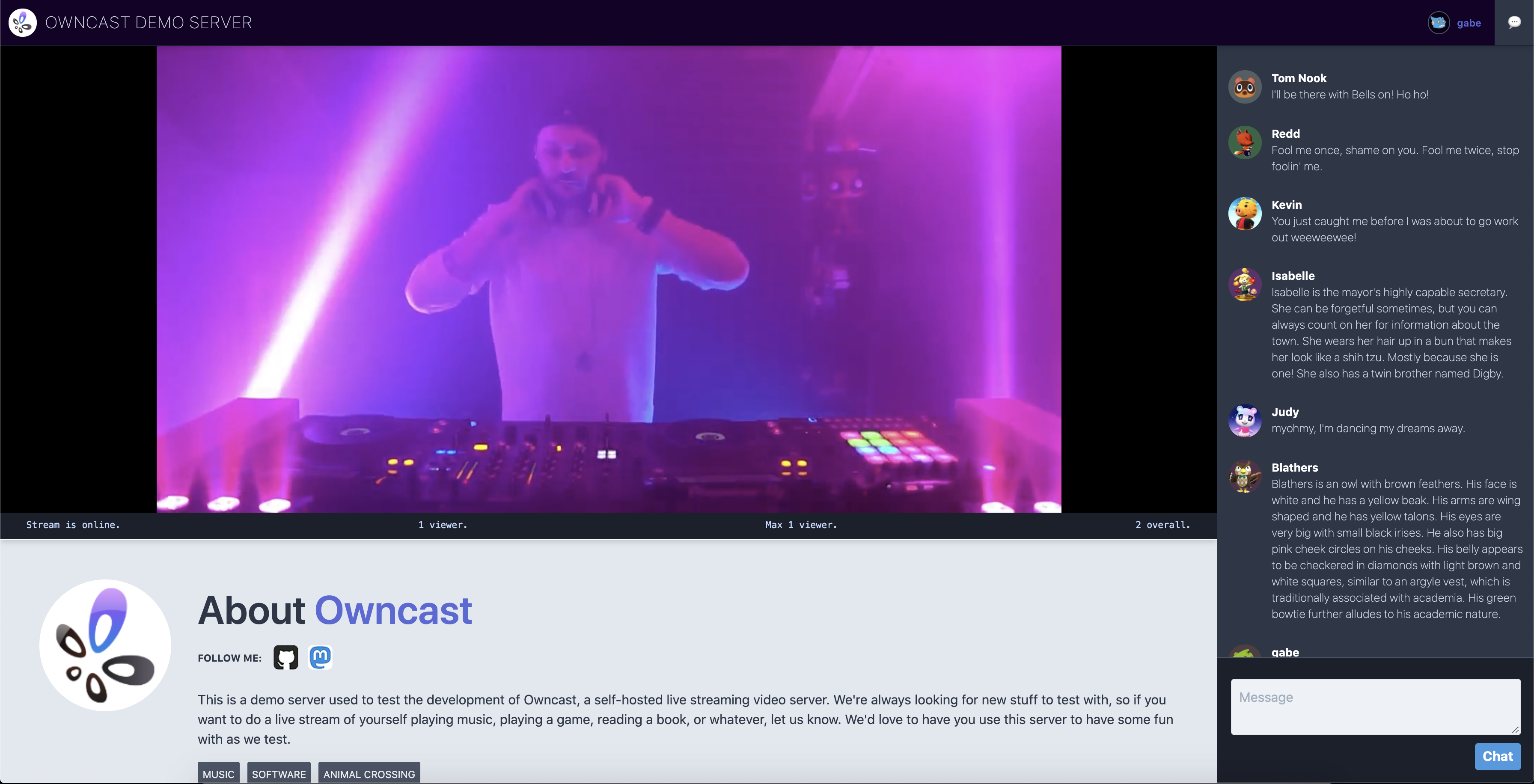
Take control over your content and stream it yourself.
Explore the docs »
View Demo
·
FAQ
.
Report Bug
Table of Contents
- About the Project
- Getting Started
- Use with your software
- Video storage and distribution options
- Building from source
- License
- Contact
About The Project
In 2020 the world changed when everyone become stuck in their homes, looking for creative outlets to share their art, skills and themselves from inside their bedroom.
This created an explosion of live streaming on Facebook Live, YouTube Live, Instagram, and Twitch. These services provided everything they needed, an easy way to live stream to the world, and a chat for users to be a part of their community.
But in a world where many were previously finding ways to rely on the big internet service companies less, the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic made everyone run right back to them.
And as soon as people started streaming their DJ sets, movie watching parties, and themselves just sitting around listening to music the big companies came to mute their streams, remove their recordings or ban these users all together.
That's when I wanted a better option for people. Something you could run yourself and get all the functionality of these services, where you could live stream to an audience and and allow them to take part in the chat, just like they've been used to on all the other services. But instead of handing control over to somebody else, you run it. You won't get shut down, and you own it all, just like it should be.
I figured you can install Wordpress and self-host your blog, or install Megento and self-host your e-commerce site. You can install Icecast and have your own internet radio station. Spin up an instance of Mastodon and you have your own social media site that you control. You can even install Nextcloud and have your own personal productivity service replacing Dropbox and Google Docs. There's an open-source alternative to all the big services that you can run for almost everything, but I couldn't think of what the live video streaming equivalent was. There should be a independent, standalone Twitch in a Box.
Keep in mind that while streaming to the big social companies is always free, you pay for it with your identity and your data, as well as the identity and data of every person that tunes in. When you self-host anything you'll have to pay with your money instead. But running a self-hosted live stream server can be done for as cheap as $5/mo, and that's a much better deal than selling your soul to Facebook, Google or Amazon.
Prerequisites
- A computer that's on the public internet to run it on. While crunching through video and serving it to viewers can be intensive from the computing side, you can get away with pretty meager resources on a simple setup. If you don't already have a server to run it on you can get a Linode instance for $5/mo that runs it fine. If you worry that you'll be maxing out the bandwidth or transfer limits allotted to you, then utilize S3 Storage very cheaply (or even free for a certain amount) to serve the files instead.
Getting Started
The goal is to have a single service that you can run and it works out of the box. Visit the Quickstart to get up and running.
Configuration
Many aspects can be adjusted and customized to your preferences. Read more about Configuration to update the web UI and video easily.
Use with your desktop software
Usage with OBS
OBS isn't required, but it's a pretty good piece of free software that will get you streaming from your own computer right away.
- Install OBS or Streamlabs OBS and get it working with your local setup.
- Open OBS Settings and go to "Stream".
- Select "Custom..." as the service.
- Enter the URL of the server running your streaming service in the format of rtmp://myserver.net/live.
- Enter your "Stream Key" that matches the key you put in your
config.yamlfile. - Start the server.
- Press "Start Streaming" (OBS) or "Go Live" (Streamlabs) on OBS.
Usage with Restream
Read the detailed documentation for working with Restream
Video storage options
Three ways of storing and distributing the video are supported.
- Locally via the built-in web server.
- S3-compatible storage.
- Experimental IPFS support.
Local file distribution
This is the simplest and works out of the box. In this scenario video will be served to the public from the computer that is running the server. If you have a fast internet connection, enough bandwidth alotted to you, and a small audience this may be fine for many people.
S3-Compatible Storage
Enable S3 support in config.yaml and add your access credentials. Files will be distributed from a S3 bucket that you have created for this purpose. This is a good option for almost any case since S3 is cheap and you don't have to worry about your own bandwidth.
Please read the more detailed documentation about configuration of S3-Compatible Services.
IPFS
From the IPFS website:
Peer-to-peer IPFS saves big on bandwidth — up to 60% for video — making it possible to efficiently distribute high volumes of data without duplication.
Enable experimental IPFS support and your video will be distributed through the IPFS network. In this scenario viewers will stream the video from IPFS nodes instead of the server running the service. This is free but can be very slow. It can also be just fine, you'll have to experiment for yourself. It can sometimes take too long for the network to get the video to the user, resulting in delays and heavy buffering. Try it if you like and make any suggestions on how to make it better so everyone can have free global video distribution without paying for a CDN or a 3rd party storage service.
By editing the config file you can change what IPFS gateway server is used, and you can experiment with trying different ones.
Building from Source
- Ensure you have the gcc compiler configured.
- Install the Go toolchain.
- Clone the repo.
git clone https://github.com/gabek/owncast - Follow the above Getting Started instructions, making sure ffmpeg exists and your config file is set.
go run main.goon the first run will download the required packages needed for the application to build.- It will start running the same as in the above Usage instructions and you can point OBS to your localhost instance of it.
License
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for more information.
Contact
Gabe Kangas - @gabek@mastodon.social - email gabek@real-ity.com
Project Link: https://github.com/gabek/owncast